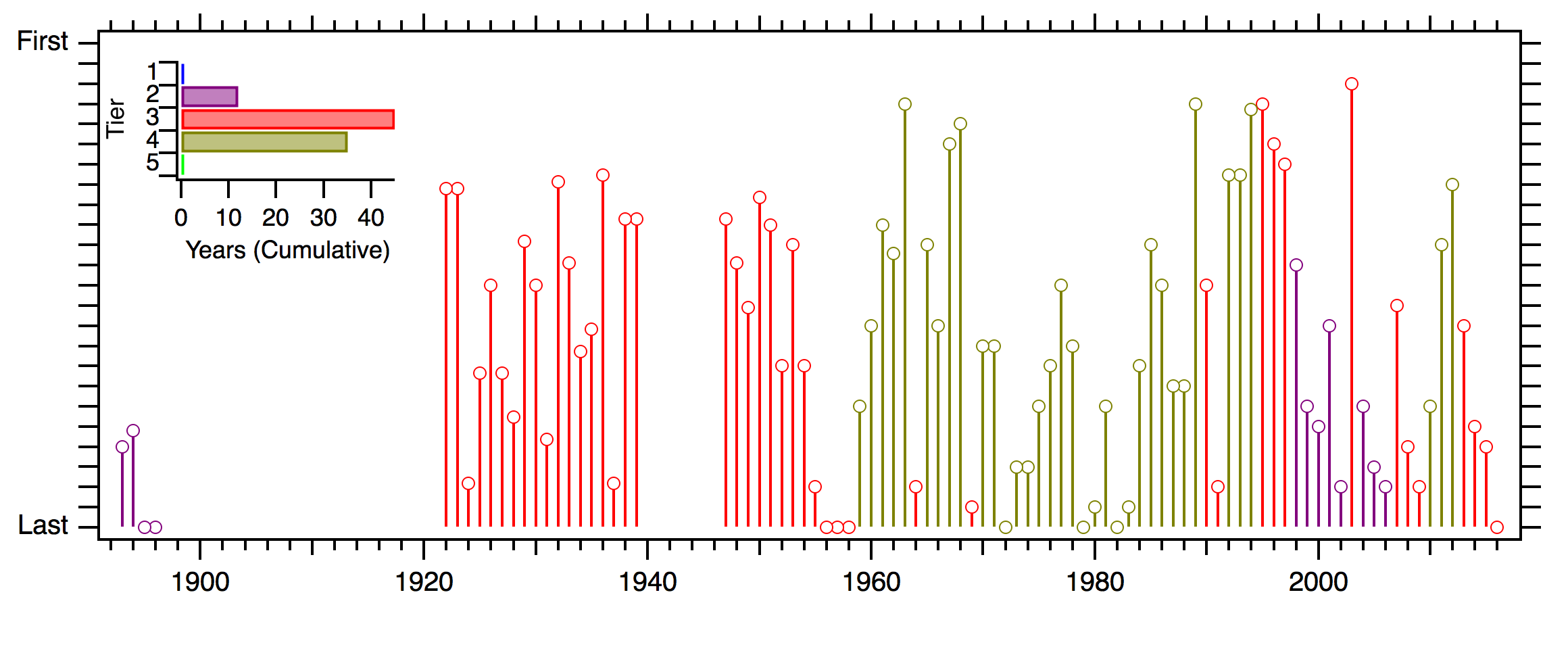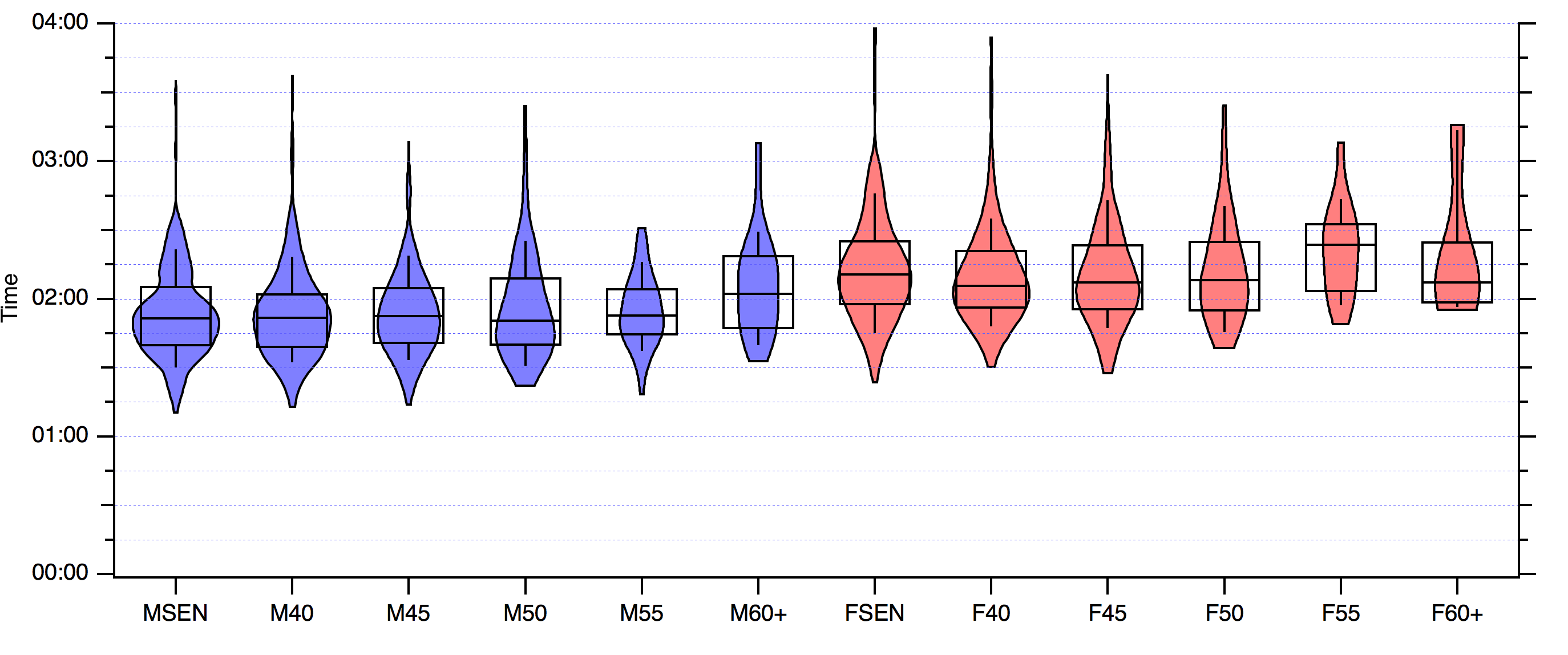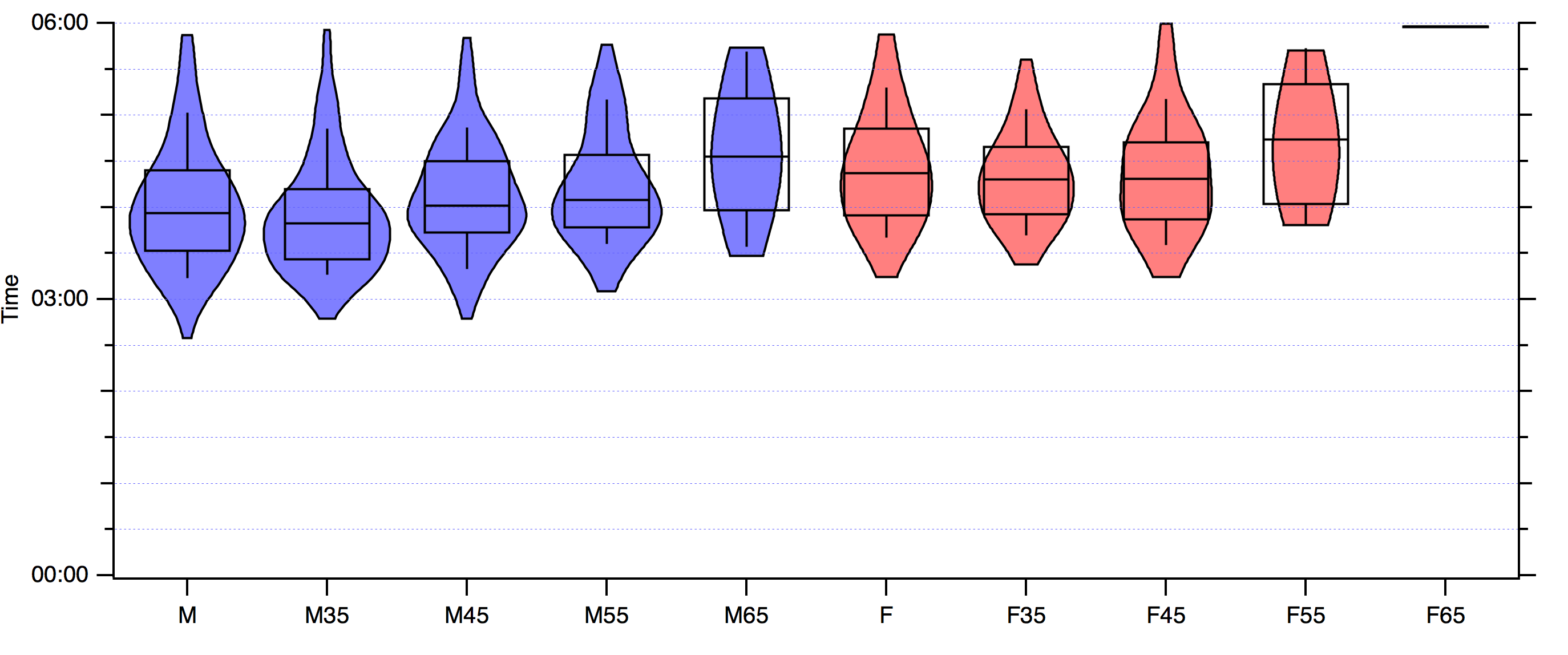
2016 was the 400 year anniversary of William Shakespeare’s death. Stratford-upon-Avon Rotary Club held the Shakespeare Marathon on the same weekend. Runners had an option of half or full marathon. There were apparently 3.5 K runners. Only 700 of whom were doing the full marathon.