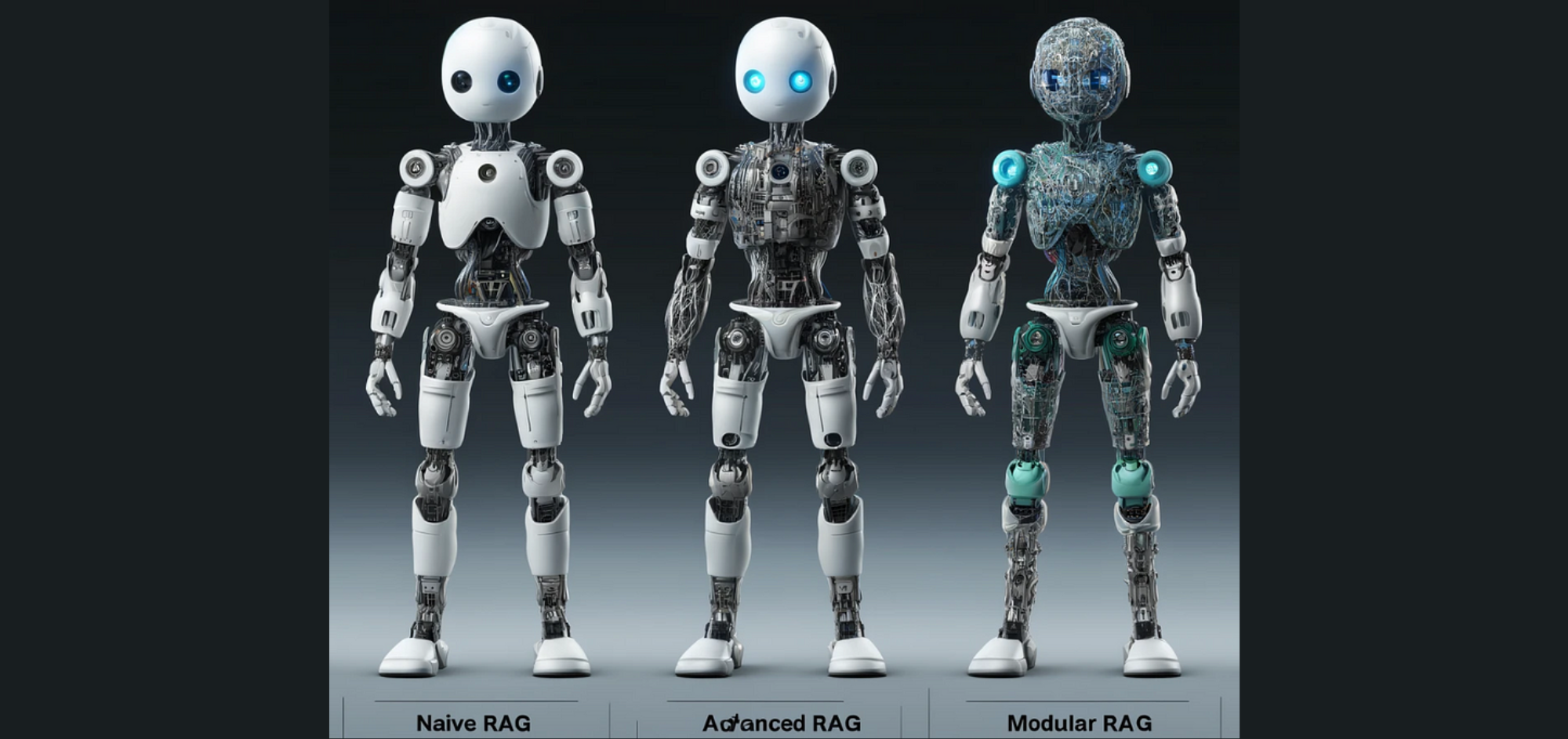
Introduction Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success. But, they still face significant limitations, especially in domain-specific or knowledge-intensive tasks such as question answering, producing “hallucinations” where the models generate responses that sound plausible but are actually incorrect when handling queries beyond their training data or requiring current information.