Chemical and engineering news (C&EN) is asking people to vote for their molecule of the year from six highlighted candidates.

Chemical and engineering news (C&EN) is asking people to vote for their molecule of the year from six highlighted candidates.
Following on from a search for long C-C bonds, here is the same repeated for C=C double bonds.
In an earlier post, I searched for small C-C-C angles, finding one example that was also accompanied by an apparently exceptionally long C-C bond (2.18Å). But this arose from highly unusual bonding giving rise not to a single bond order but one closer to one half!

Another conference, a Cambridge satellite meeting of OpenCon, and I quote here its mission: “OpenCon is a platform for the next generation to learn about Open Access, Open Education, and Open Data, develop critical skills, and catalyze action toward a more open system of research and education” targeted at students and early career academic professionals.
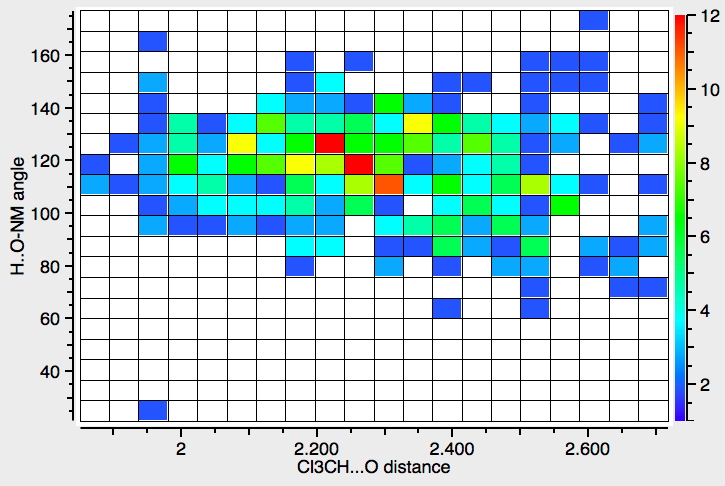
Chloroform, often in the deuterated form CDCl3, is a very common solvent for NMR and other types of spectroscopy. Quantum mechanics is increasingly used to calculate such spectra to aid assignment and the solvent is here normally simulated as a continuum rather than by explicit inclusion of one or more chloroform molecules.
This is sent from the Pidapalooza event in Reykjavik, Iceland, and is a short collection of notable things I learnt or which attracted my attention.
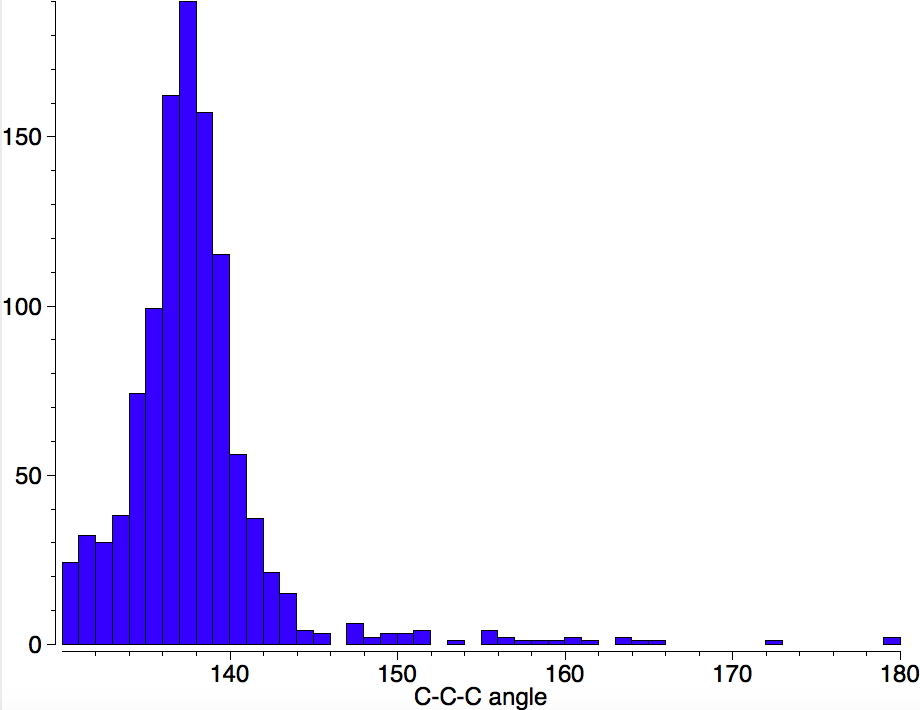
I am now inverting the previous question by asking what is the largest angle subtended at a chain of three connected 4-coordinate carbon atoms? Let’s see if further interesting chemistry can be unearthed.
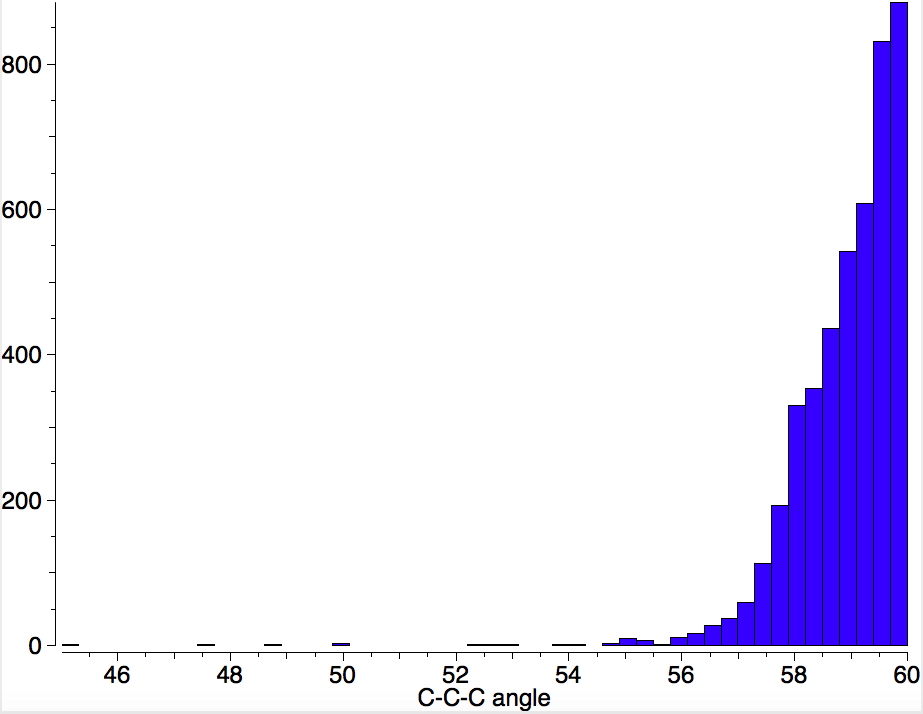
Is asking a question such as “what is the smallest angle subtended at a chain of three connected 4-coordinate carbon atoms” just seeking another chemical record, or could it unearth interesting chemistry?
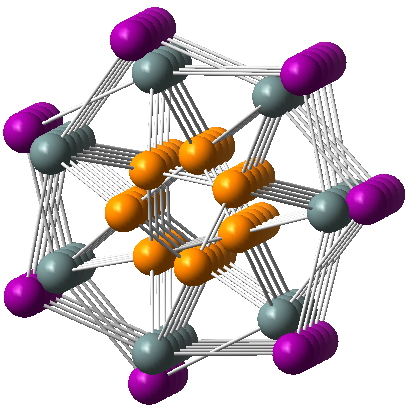
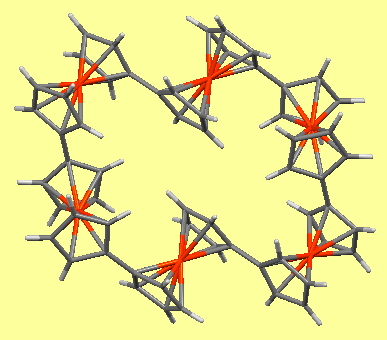
After sixty years of searching, the first non-templated double helical carbon-free inorganic molecular structure has been reported. That is so neat that I thought to load the 3D coordinates here for you to interact with and then to explore the prospect of using these coordinates to add some value with e.g. some chiroptical calculations.
Chemists are as fond of records as any, although I doubt you will find many chemical ones in the Guinness world records list. Polytriangulanes chase how many cyclopropyl 3-rings can be joined via a vertex.
Previously, a mechanistic twist to the oxidation of imines using peracid had emerged. Time to see how substituents respond to this mechanism.