In the previous post, I introduced three of a new generation of search engines specialising in the discovery of data.
Chemists have long been familiar with search engines that aspire to index a large proportion of the chemical literature.
In the previous post, I looked at the mechanism for 1,4-nucleophilic addition to an activated alkene (the Michael reaction). The model nucleophile was malonaldehyde after deprotonation and the model electrophile was acrolein (prop-2-enal), with the rate determining transition state being carbon-carbon bond formation between the two, accompanied by proton transfer to the oxygen of the […]
In 2013, I created an iTunesU library of 115 mechanistic types in organic and organometallic chemistry, illustrated using video animations of the intrinsic reaction coordinate (IRC) computed using a high level quantum mechanical procedure. Many of those examples first derived from posts here.
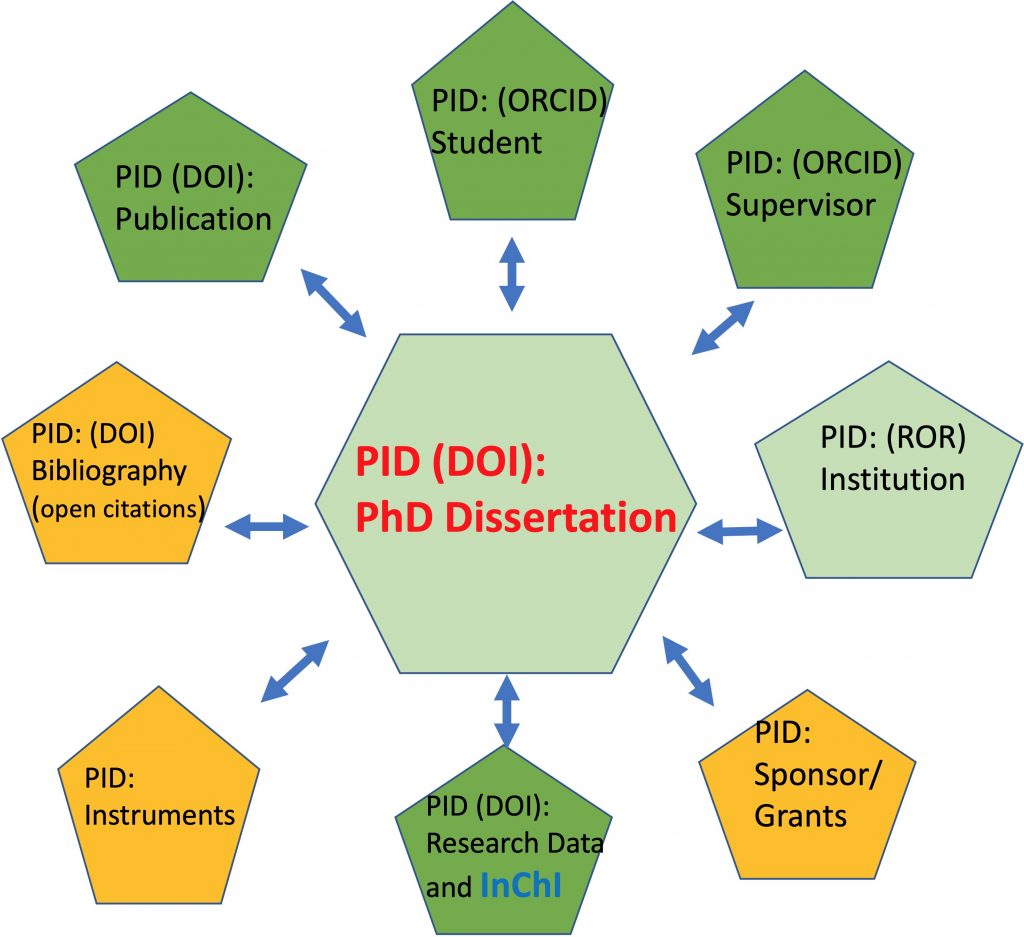
A PID or persistent identifier has been in common use in scientific publishing for around 20 years now. It was introduced as a DOI (Digital Object Identifier), and the digital object in this case was the journal article.
In 2001, Shaik and co-workers published the first of several famous review articles on the topic A Different Story of π-Delocalization. The Distortivity of π-Electrons and Its Chemical Manifestations.
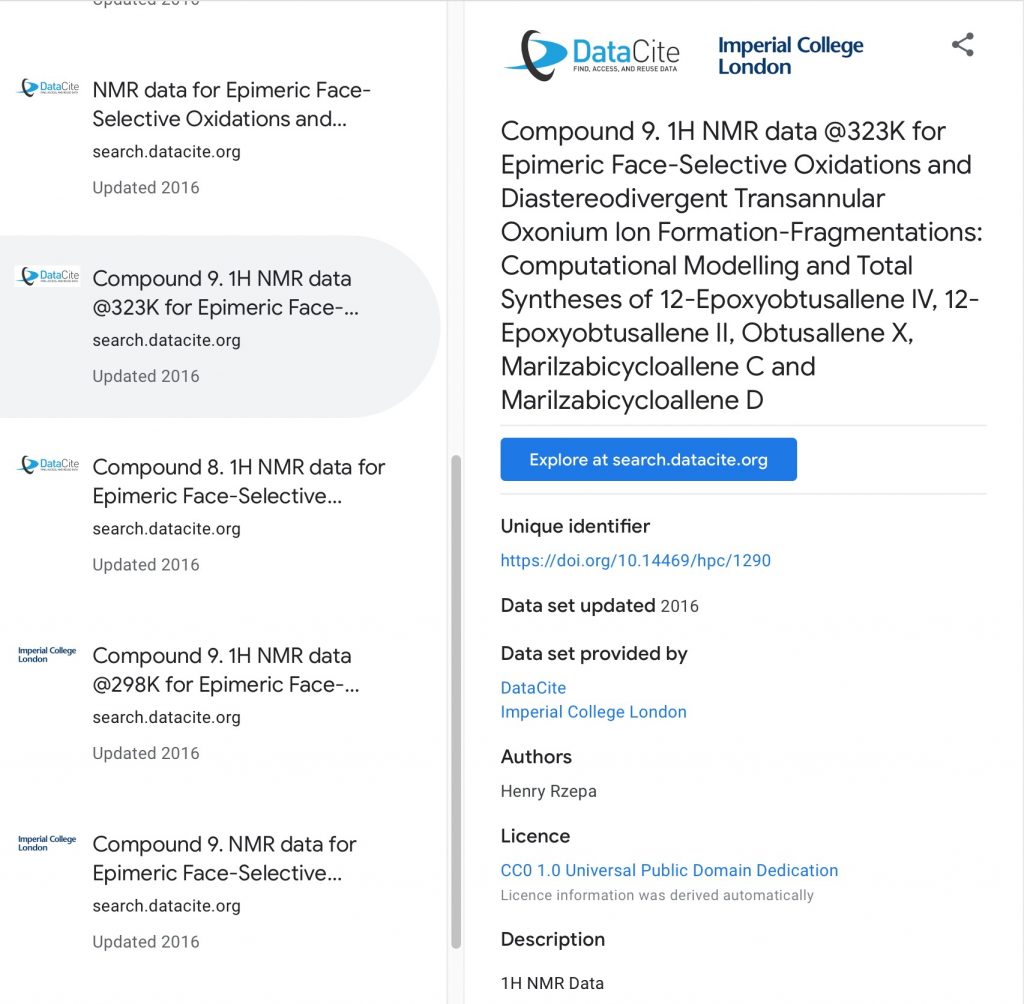
In a welcome move, one of the American chemical society journals has published an encouragement to submit what is called FAIR data to the journal.. A reminder that FAIR data is data that can be Found (F), Accessed (A), Interoperated(I) and Re-used( R). I thought I might try to explore this new tool here.
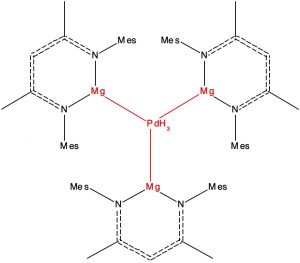
Here is another selection from the Molecules-of-the-Year shortlist published by C&E News, in which hexagonal planar transition metal coordination is identified.
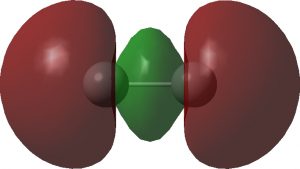
I noted in an earlier blog, a potential (if difficult) experimental test of the properties of the singlet state of dicarbon, C2. Now, just a few days ago, a ChemRxiv article has been published suggesting another (probably much more realistic) test. This looks at the so-called 7Σ open shell state of the molecule where three electrons […]
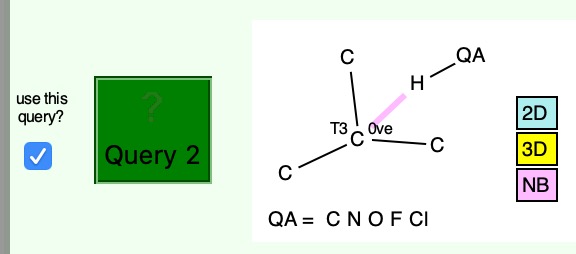
Having shown that carbon as a carbene centre, C: can act as a hydrogen bond acceptor, as seen from a search of crystal structures, I began to wonder if there is any chance that carbon as a radical centre, C• could do so as well. Definitely a subversive thought, since radical centres are supposed to abstract hydrogens […]
In the previous post, I showed that carbon can act as a hydrogen bond acceptor (of a proton) to form strong hydrogen bond complexes. Which brings me to a conceptual connection: can singlet dicarbon form such a hydrogen bond?