Calicheamicin was noted in the previous post as a natural product with antitumour properties and having many weird structural features such as an unusual “enedidyne” motif. The representation is shown below. A partial structure shown below for Calicheamicin replaces the -(CH 2 )4- substructure with a four carbon chain that includes two sp 2 centres instead of two sp 3 centres.
Calicheamicin is a natural product with antitumour properties discovered in the 1980s, with the structure shown below. As noted elsewhere, this structure has many weird properties, including amongst other features an unusual “enedidyne” motif and the presence of an iodo group on an aromatic ring.
The Masamune-Bergman reaction[cite]10.1039/C29710001516[/cite],[cite]10.1021/ja00757a071[/cite] is an example of a highly unusual class of chemical mechanism[cite]10.1021/cr4000682[/cite] involving the presumed formation of the biradical species shown as Int1 below by cyclisation of a cycloenediyne reactant. Such a species is so reactive that it will be quickly trapped, as for example by dihydrobenzene to form

Back in 2017, I was asked to peer review an article and its author asked if I would like the review to be “open” – that is that my name would be shown as a reviewer; [cite]10.1073/pnas.1709586114[/cite/] indeed it was!

Metadata is something that goes on behind the scenes and is rarely of concern to either author or readers of scientific articles. Here I tell a story where it has rather greater exposure. For journals in science and chemistry, each article published has a corresponding metadata record, associated with the persistent identifier of the article and known to most as its DOI.
I should start by saying that the server on which this blog is posted was set up in June 1993. Although the physical object has been replaced a few times, and had been “virtualised” about 15 years ago, a small number of the underlying software base components may well date way back, perhaps even to 1993.
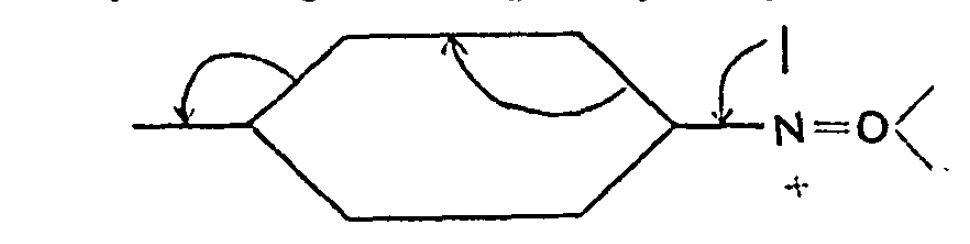
Chemists now use the term “curly arrows” as a language to describe the electronic rearrangements that occur when a (predominately organic) molecule transforms to another – the so called chemical reaction. It is also used to infer, via valence bond or resonance theory, what the mechanistic implications of that reaction are.
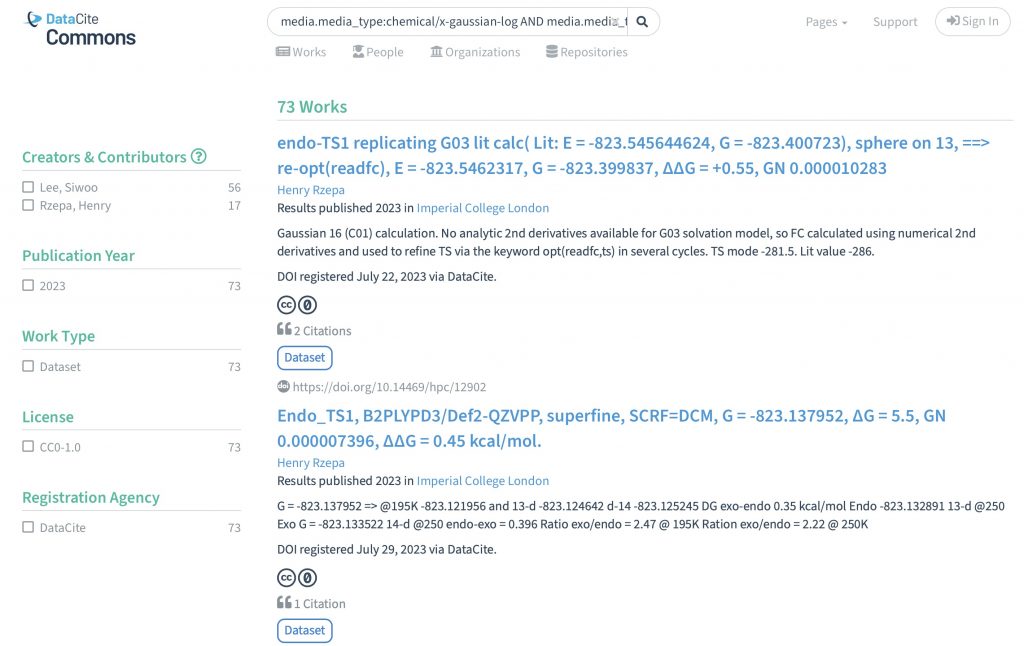
I can remember a time when journal articles carried selected data within their body as e.g. Tables, Figures or Experimental procedures, with the rest consigned to a box of paper deposited (for UK journals) at the British library. Then came ESI or electronic supporting information.
In the previous post, I explored the so-called “impossible” molecule methanetriol. It is regarded as such because the equilbrium resulting in loss of water is very facile, being exoenergic by ~14 kcal/mol in free energy. Here I explore whether changing the substituent R could result in suppressing the loss of water and stabilising the triol.
What constitutes an “impossible molecule”? Well, here are two, the first being the topic of a recent article[cite]10.1021/jacs.4c02637[/cite]. The second is a favourite of organic chemistry tutors, to see if their students recognise it as an unusual (= impossible) form of a much better known molecule. Perhaps we could define impossible molecules into two slightly different classes.
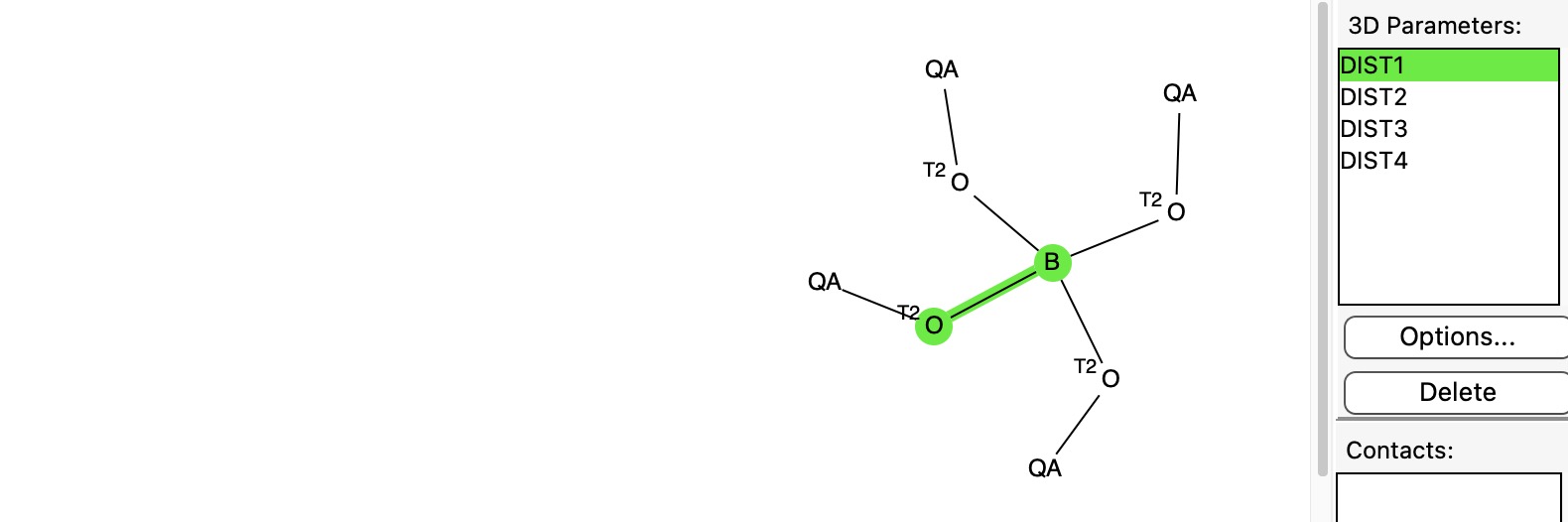
In an earlier post, I discussed[cite]10.59350/dfkt5-k2b20[/cite] a phenomenon known as the “anomeric effect” exhibited by tetrahedral carbon compounds with four C-O bonds. Each oxygen itself bears two bonds and has two lone pairs, and either of these can align with one of three other C-O bonds to generate an anomeric effect. Here I change the central carbon to a boron to explore what happens, as indeed I promised earlier.
