Consider acetaldehyde (ethanal for progressive nomenclaturists). What conformation does it adopt, and why? This question was posed of me by a student at the end of a recent lecture of mine. Surely, an easy answer to give?
In a previous post, I set out how to show how one can reduce a 1H NMR spectrum to the structure [A] below. I speculated how a further test could be applied to this structure; back predicting its spectrum using just quantum mechanics. Overkill I know, but how well might the two match?
The electronic interaction between a single bond and an adjacent double bond is often called σ-π-conjugation (an older term for this is hyperconjugation), and the effect is often used to e.g. explain why more highly substituted carbocations are more stable than less substituted ones.
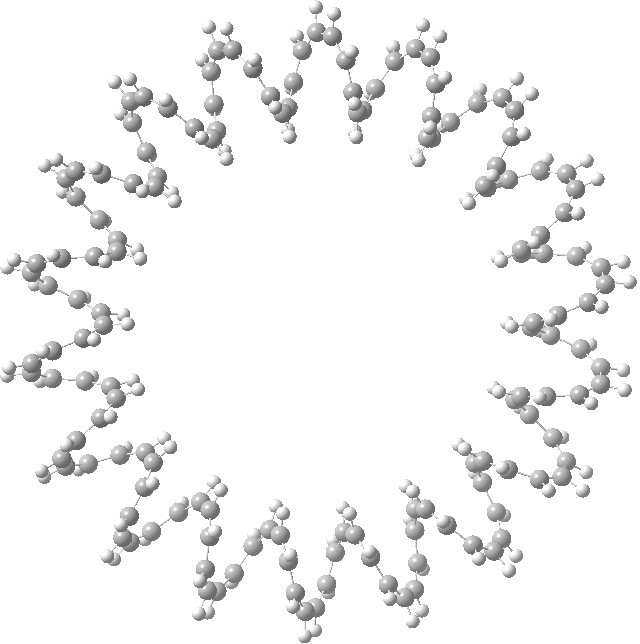
This is a recently published (hypothetical) molecule which has such unusual properties that I cannot resist sharing it with you. It is an annulene with 144 all-cis CH groups, being a (very) much larger cousin of (also hypothetical) systems mooted in 2009,.
It is always rewarding when one comes across a problem in chemistry that can be solved using a continuous stream of rules and logical inferences from them. The example below is one I have been using as a tutor in organic chemistry for a few years now, and I share it here.
Although have dealt with the π-complex formed by protonation of PhNHOPh in several posts, there was one aspect that I had not really answered; what is the most appropriate description of its electronic nature? Here I do not so much provide an answer, as try to show how difficult getting an accurate answer might be.
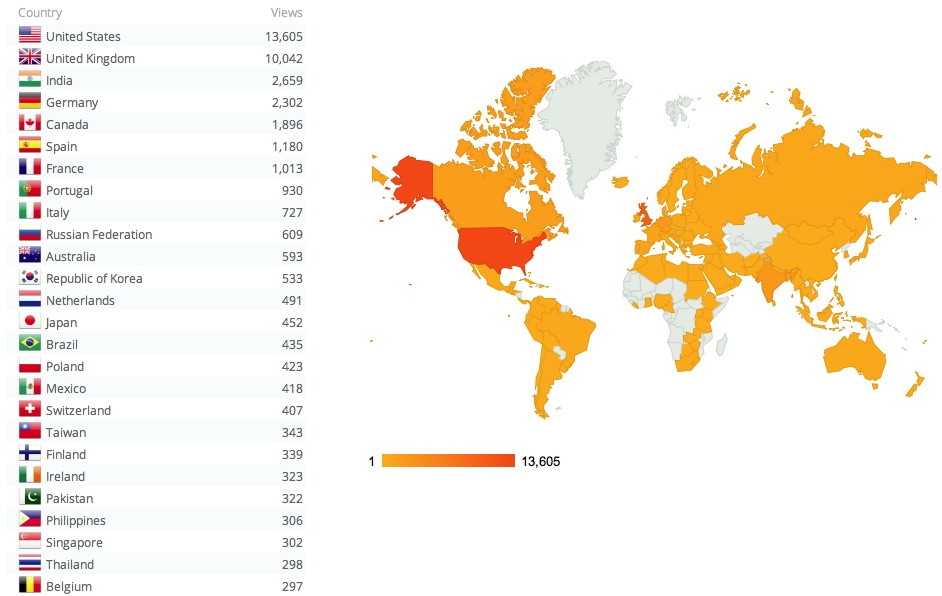
With metrics in science publishing controversial to say the least, I pondered whether to write about the impact/influence a science-based blog might have (never mind whether it constitutes any measure of esteem). These are all terms that feature large when an (academic) organisation undertakes a survey of its researchers’ effectiveness.‡ WordPress (the organisation that provides the […]
The transient π-complex formed during the “[5,5]” sigmatropic rearrangement of protonated N,O-diphenyl hydroxylamine can be (formally) represented as below, namely the interaction of a six-π-electron aromatic ring (the phenoxide anion 2) with a four-π-electron phenyl dication-anion pair 1. Can one analyse this interaction in terms of aromaticity?
Michael Dewar famously implicated a so-called π-complex in the benzidine rearrangement, back in the days when quantum mechanical calculations could not yet provide a quantitatively accurate reality check. Because this π-complex actually remains a relatively unusual species to encounter in day-to-day chemistry, I thought I would try to show in a simple way how it forms.
If you search e.g. Scifinder for N,O-diphenyl hydroxylamine (RN 24928-98-1) there is just one literature citation, to a 1962 patent. Nothing else;
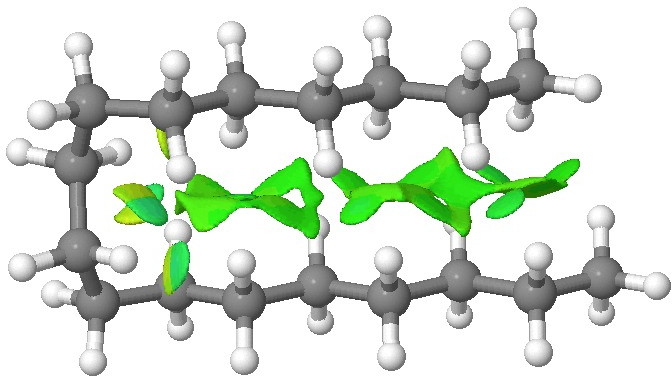
We tend to think of simple hydrocarbons as relatively inert and un-interesting molecules.