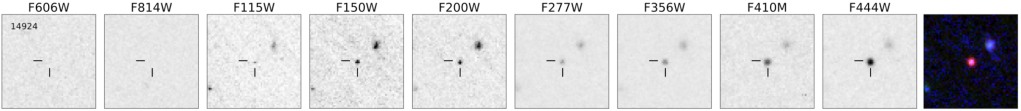
I was raised to believe that it was rude to tell people I told you so . Yet that’s pretty much the essence of the scientific method: we test hypotheses by making predictions, then checking to see which told us the correct result in advance of the experiment. So: I told you so. Our paper on massive galaxies at high redshift is out in the Astrophysical Journal today.
I just got back from a visit to the Carnegie Institution of Washington where I gave a talk and saw some old friends. I was a postdoc at the Department of Terrestrial Magnetism (DTM) in the ’90s. DTM is so-named because in their early days they literally traveled the world mapping the magnetic field. When I was there, DTM + had a small extragalactic astronomy group including Vera Rubin*, Francois Schweizer, and John Graham.
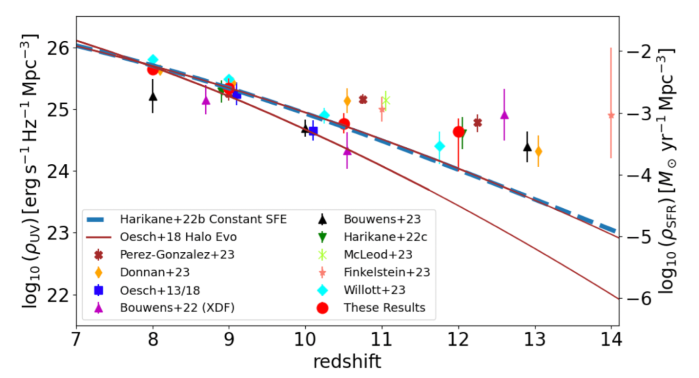
The results from the high redshift universe keep pouring in from JWST. It is a full time job, and then some, just to keep track. One intriguing aspect is the luminosity density of the universe at z > 10. I had not thought this to be problematic for LCDM, as it only depends on the overall number density of stars, not whether they’re in big or small galaxies. I checked this a couple of years ago, and it was fine.
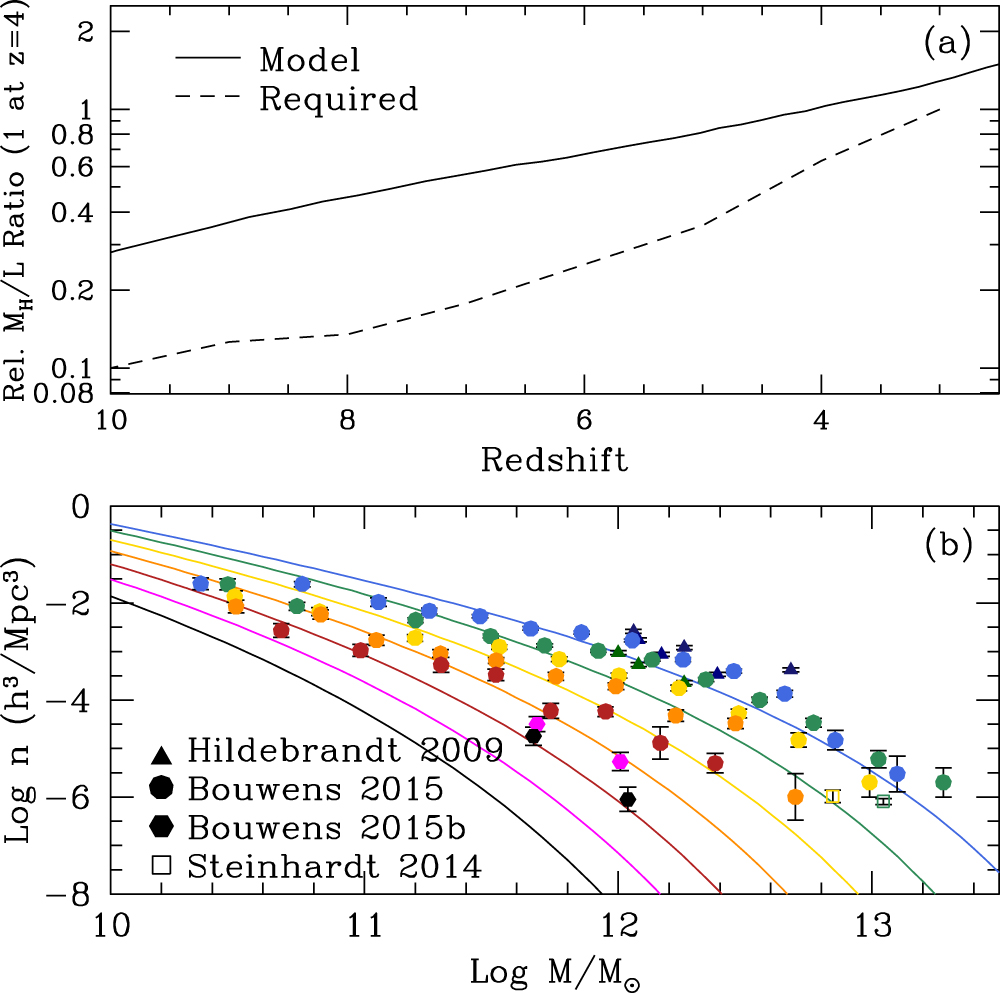
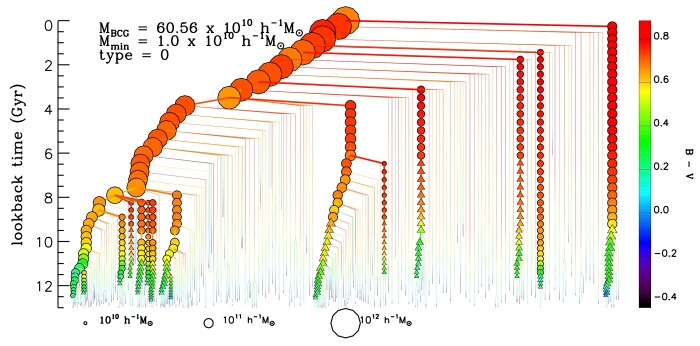
As predicted, JWST has been seeing big galaxies at high redshift. There are now many papers on the subject, ranging in tone from “this is a huge problem for LCDM” to “this is not a problem for LCDM at all” – a dichotomy that persists. So – which is it? It will take some time to sort out. There are several important aspects to the problem, one of which is agreeing on what LCDM actually predicts.

To start the new year, I provide a link to a discussion I had with Simon White on Phil Halper’s YouTube channel: In this post I’ll say little that we don’t talk about, but will add some background and mildly amusing anecdotes. I’ll also try addressing the one point of factual disagreement. For the most part, Simon & I entirely agree about the relevant facts; what we’re discussing is the interpretation of those facts.

This clickbait title is inspired by the clickbait title of a recent story about high redshift galaxies observed by JWST. To speak in the same vernacular: LOL! What they mean, as I’ve discussed many times here, is that it is difficult to explain these observations in LCDM. LCDM does not encompass all of science. Science * predicted exactly this.

Cosmology is challenged at present by two apparently unrelated problems: the apparent formation of large galaxies at unexpectedly high redshift observed by JWST, and the tension between the value of the Hubble constant obtained by traditional methods and that found in multi-parameter fits to the acoustic power spectrum of the cosmic microwave background (CMB). Maybe they’re not unrelated?
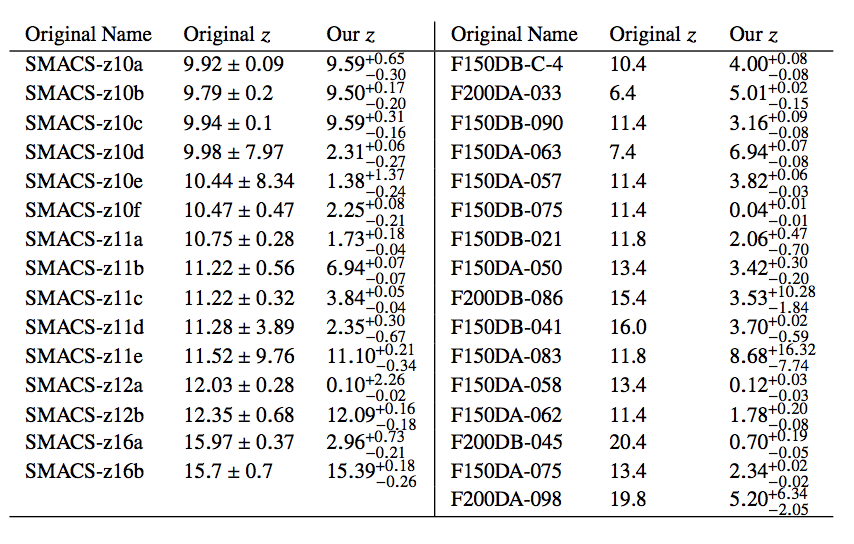
I noted last time that in the rush to analyze the first of the JWST data, that “some of these candidate high redshift galaxies will fall by the wayside.” As Maurice Aabe notes in the comments there, this has already happened. I was concerned because of previous work with Jay Franck in which we found that photometric redshifts were simply not adequately precise to identify the clusters and protoclusters we were looking for.

I went on a bit of a twitter bender yesterday about the early claims about high mass galaxies at high redshift, which went on long enough I thought I should share it here. For those watching the astro community freak out about bright, high redshift galaxies being detected by JWST, some historical context in an amusing anecdote… The 1998 October conference was titled “After the dark ages, when galaxies were young (the universe at 2 < z <