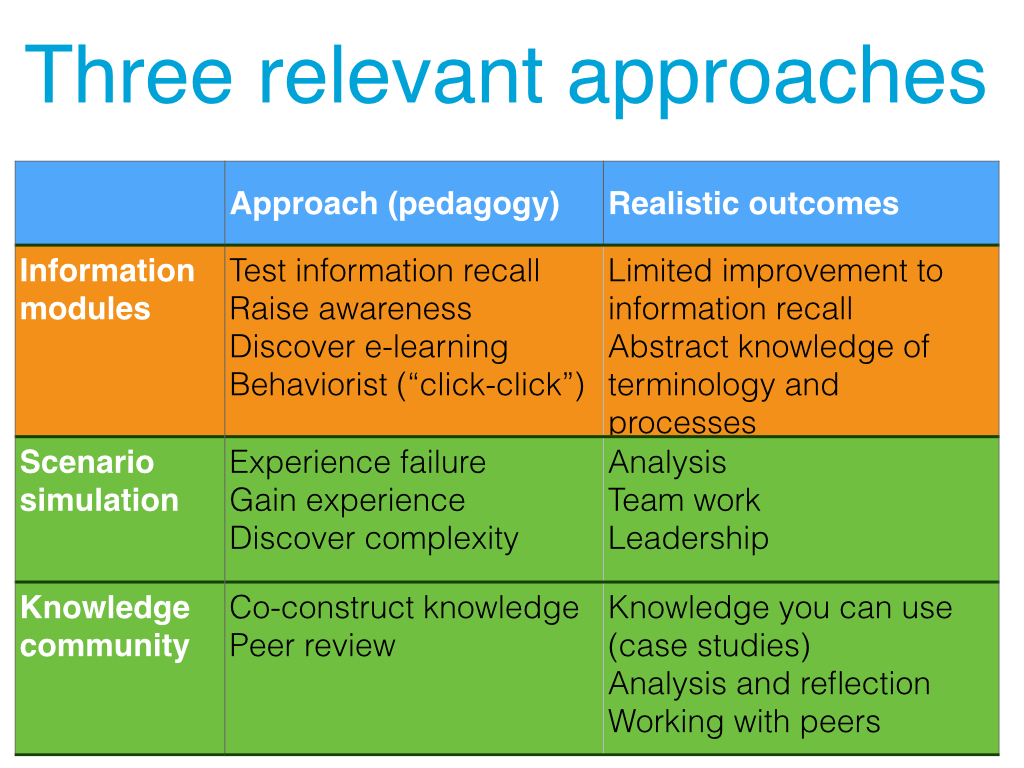
As much as I wish this blog could document my reflections as I read, research, speak, and listen… it cannot. Knowledge is a process, not a product, in this VUCA world we live in. I know that I am doing too much, too fast, to be ale to process everything. Accepting this is part and parcel of navigating the knowledge landscape. So here is an incomplete round-up with some schematic thoughts about where I’m headed.