The mechanism of forming an oxime from nucleophilic addition of a hydroxylamine to a ketone is taught early on in most courses of organic chemistry. Here I subject the first step of this reaction to form a tetrahedral intermediate to quantum mechanical scrutiny.
Semibullvalene is a molecule which undergoes a facile [3,3] sigmatropic shift. So facile that it appears this equilibrium can be frozen out at the transition state if suitable substituents are used. This is a six-electron process, which leads to one of those homologous questions; what happens with ten electrons?
The four-electron thermal cycloaddition (in reverse a cheletropic elimination) of dichlorocarbene to ethene is a classic example of a forbidden pericyclic process taking a roundabout route to avoid directly violating the Woodward-Hoffmann rules.
I am following up on one unfinished thread in my previous post; a candidate was proposed in which the transition state for [3,3] sigmatropic rearrangement in a semibullvalene might be frozen out to become instead a stable minimum.
Semibullvalene is an unsettling molecule. Whilst it has a classical structure describable by a combination of Lewis-style two electron and four electron bonds, its NMR behaviour reveals it to be highly fluxional. This means that even at low temperatures, the position of these two-electron bonds rapidly shifts in the equilibrium shown below.
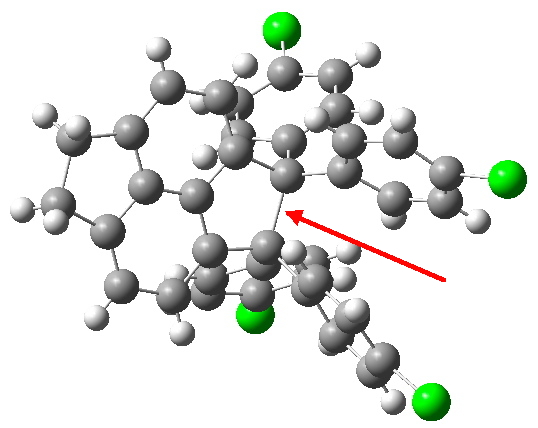
Here is a challenge: what is the longest C-C bond actually determined (in which both carbon termini are sp3 hybridised)? I pose this question since Steve Bachrach has posted on how to stabilize long bonds by attractive dispersive interactions, and more recently commenting on what the longest straight chain alkane might be before dispersive interaction start […]
All organic chemists are familiar with the stereochemical notation for bonds, as shown below. But I had difficulty tracking down when it was introduced, and by whom. I offer a suggestion here, but if anyone reading this blog has got a better/earlier attribution, please let us know!
An obvious issue to follow-up my last post on the (solvated) intrinisic reaction coordinate for the Sn2 reaction is how variation of the halogen (X) impacts upon the nature of the potential.
It was three years ago that I first blogged on the topic of the Sn2 reaction. Matthias Bickelhaupt had suggested that the Sn2 reaction involving displacement at a carbon atom was an anomaly; the true behaviour was in fact exhibited by the next element down in the series, silicon.
A third digital repository has been added to the two I described before. Chempound is a free open-source repository which (unlike DSpace and Figshare) was developed specifically for chemistry.
This reaction looks simple but is deceptively complex.