Twenty years are acknowledged to be a long time in Internet/Web terms.

I was first taught curly arrow pushing in 1968, and have myself taught it to many a generation of student since. But the other day, I learnt something new.
In the preceding post, I described a fascinating experiment and calculation by Bogle and Singleton, in which the trajectory distribution of molecules emerging from a single transition state was used to rationalise the formation of two isomeric products 2 and 3. In the present post, I explore possible consequences of including a sodium cation (X=Na+ below) in […]
Singleton and co-workers have produced some wonderful work showing how dynamic effects and not just transition states can control the outcome of reactions. Steve Bachrach’s blog contains many examples, including this recent one.
Years ago, I was travelling from Cambridge to London on a train. I found myself sitting next to a chemist, and (as chemists do), he scribbled the following on a piece of paper. When I got to work the next day Vera (my student) was unleashed on the problem, and our thoughts were published.
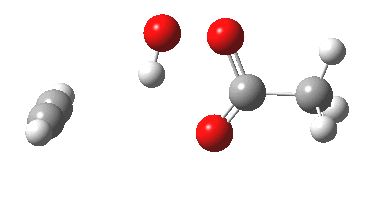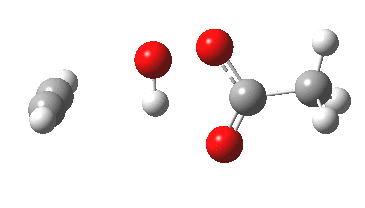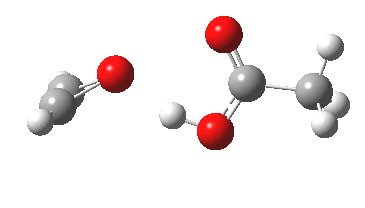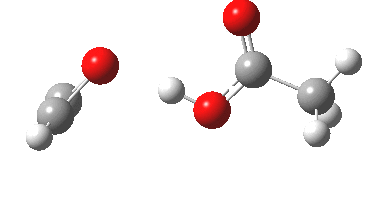
Sometimes, connections between different areas of chemistry just pop out (without the help of semantic web tools, this is called serendipity). So here, I will try to join up some threads which emerge from previous posts.
Back in 1994, we published the crystal structure of the molecule below (X=H), a putative anti-malarial drug called halofantrine. Little did we realise that a whole area of organo catalysis based on a thiourea catalyst with a similar motif would emerge a little later. Here is how the two are connected.
The reaction between a carbene and an alkene to form a cyclopropane is about as simple a reaction as one can get. But I discussed before how simple little molecules (cyclopropenyl anion) can hold surprises.
This is a continuation of the previous post exploring the transition state geometries of various types of ring closure as predicted by Baldwin’s rules. I had dealt with bond formation to a trigonal (sp2) carbon; now I add a digonal (sp) example (see an interesting literature variation).
The Baldwin rules for ring closure follow the earlier ones by Bürgi and Dunitz in stating the preferred angles of nucleophilic (and electrophilic) attack in bond forming reactions, and are as famous for the interest in their exceptions as for their adherence.
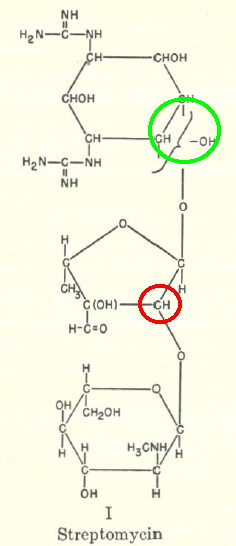
Streptomycin is an antibiotic active against tuberculosis, and its discovery has become something of a cause célèbre. It was first isolated on October 19, 1943 by a graduate student Albert Schatz in the laboratory of Selman Waksman at Rutgers University. I want to concentrate in this post on its molecular structure.