As a personal retrospective of my use of computers (in chemistry), the Macintosh plays a subtle role.
Computers and I go back a while (44 years to be precise), and it struck me (with some horror) that I have been around them for ~62% of the modern computing era (Babbage notwithstanding, ~1940 is normally taken as the start of the modern computing era). So indulge me whilst I record this perspective from […]
A scalemic molecule is the term used by Eliel to describe any non-racemic chiral compound.
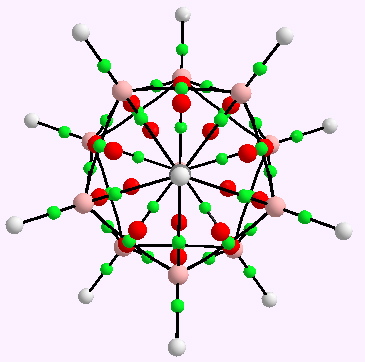
A little while ago, I speculated (blogs are good for that sort of thing) about hexavalent carbon, and noted how one often needs to make (retrospectively) obvious connections between two different areas of chemistry. That post has attracted a number of comments in the two years its been up, along the lines: what about carboranes?
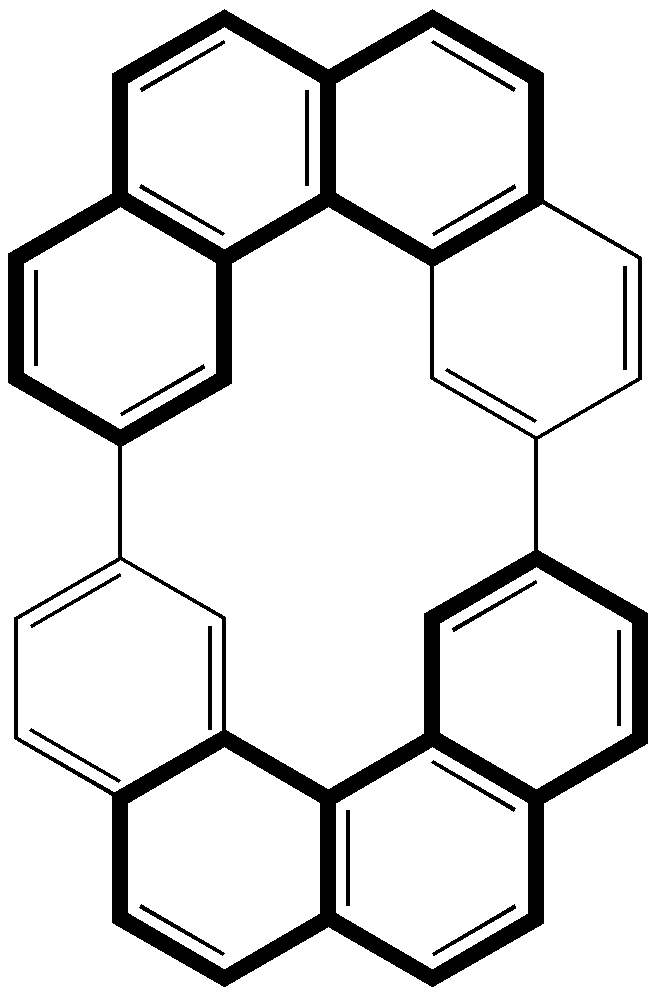
It is not often that an article on the topic of illusion and deception makes it into a chemical journal. Such is addressed (DOI: 10.1002/anie.201102210) in no less an eminent journal than Angew Chemie.
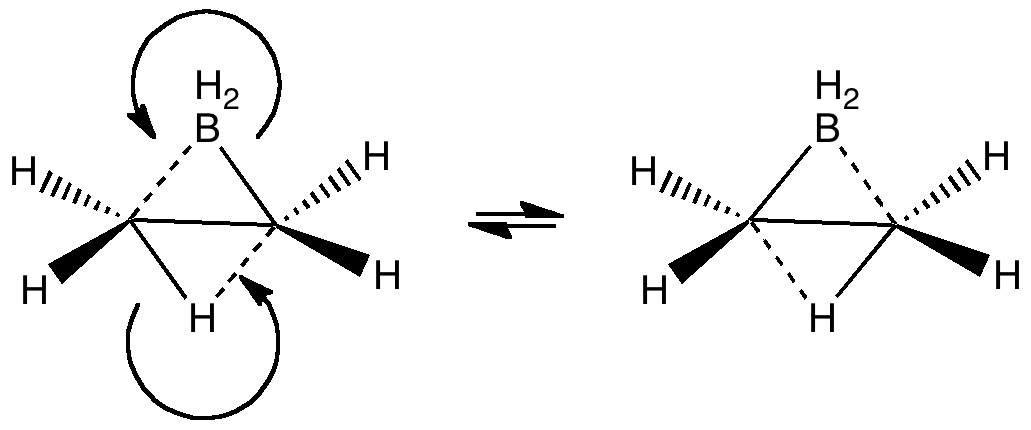
The last two posts have played a game of find the electrons. We saw how the dyotropic rearrangement of ethane borrowed electrons from the C-C bond, and how 1,2,dibromoethane went ionic on us. How about this mixed system, in which a hydrogen and a BH2 swap their positions?

In the previous post, I discussed what we could learn from ethane by forcing it into a pericyclic dyotropic rearrangement. We saw how it voraciously scavenged two electrons from the C-C bond to achieve this. What if we give it more electrons? Thus 1,2-dibromoethane undergoing the same reaction.
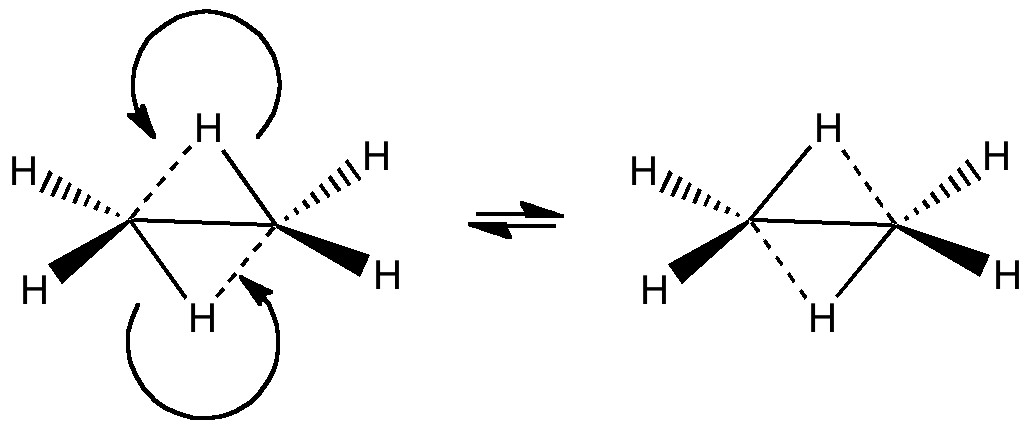
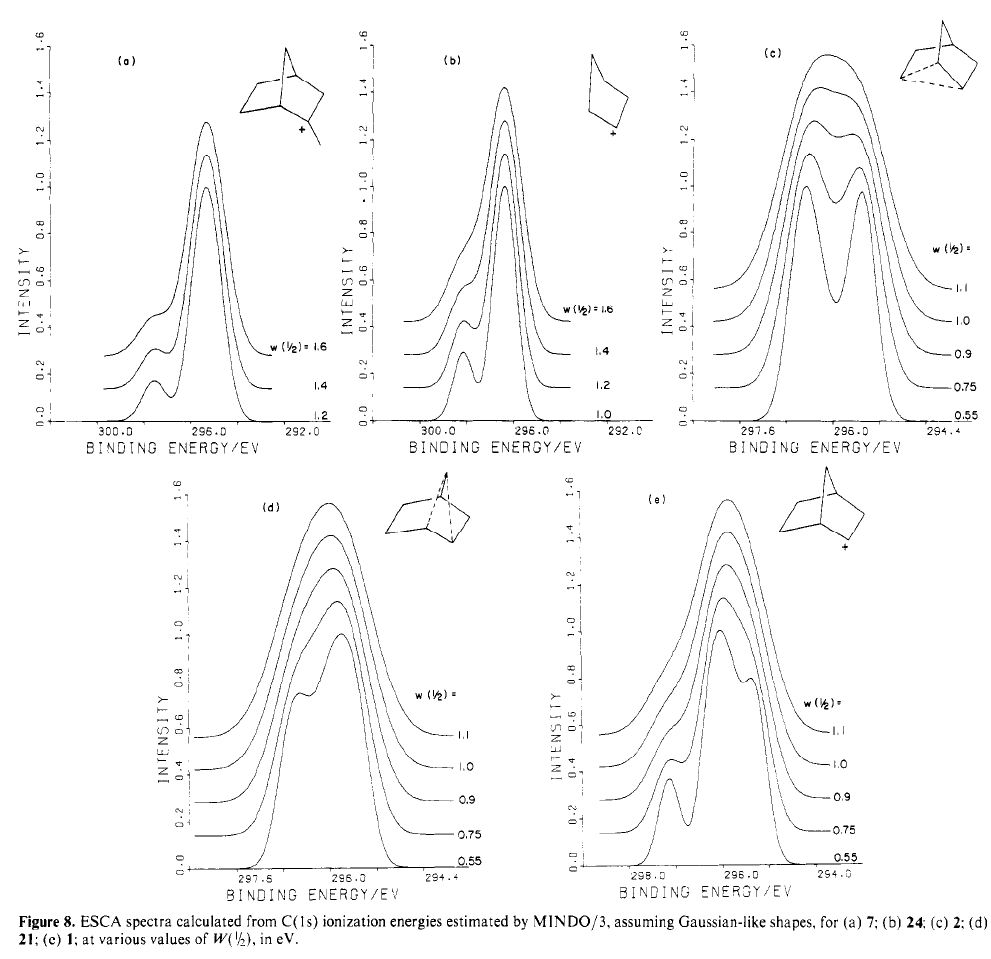
In a time when large (molecules) are considered beautiful (or the corollary that beauty must be big), it is good to reflect that small molecules may teach us something as well. Take ethane. Is there anything left which has not been said about it already?
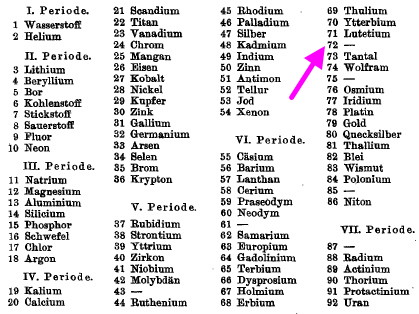
In 1923, Coster and von Hevesy claimed discovery of the element Hafnium, atomic number 72 (latin Hafnia, meaning Copenhagen, where the authors worked) on the basis of six lines in its X-ray spectrum. The debate had long raged as to whether (undiscovered) element 72 belonged to the rare-earth group 3 of the periodic table below yttrium, or whether […]
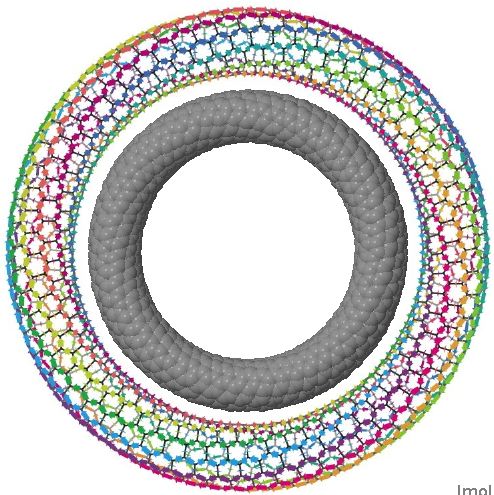
The interface between physics, chemistry (and materials science) can be a fascinating one. Here I show a carbon nanotorus, devised by physicists a few years ago. It is a theoretical species, and was predicted to have a colossal paramagnetic moment.
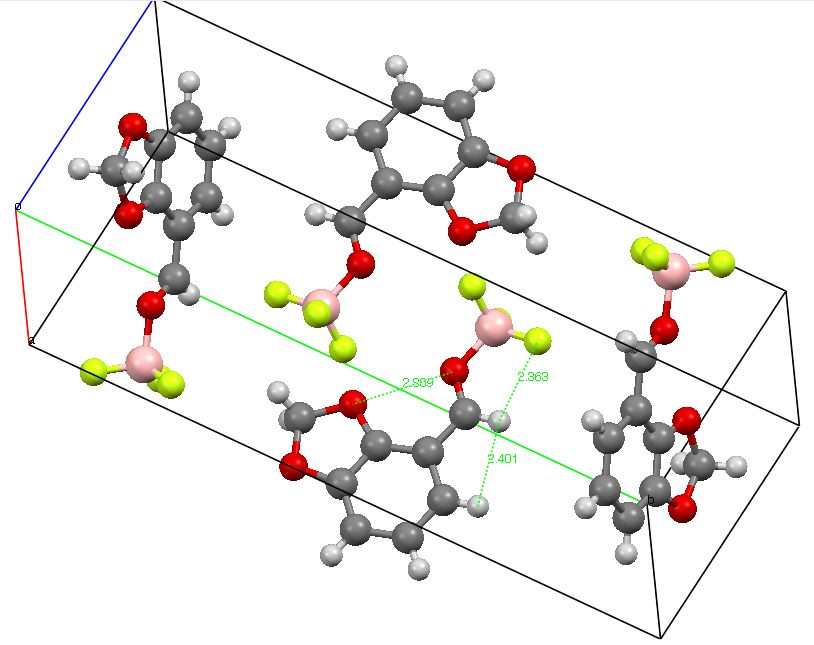
The title of this post paraphrases E. J. Corey’s article in 1997 (DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(96)02248-4) which probed the origins of conformation restriction in aldehydes. The proposal was of (then) unusual hydrogen bonding between the O=C-H…F-B groups.