Content classification is the most fundamental form of holistic content understanding. It helps make your resources findable (F2) and connects them to other resources (I3). Content understanding represents each piece of content in the index. Relevance of content is a function of query and content understanding. Query understanding represents each search query as a search intent.
Donny Winston
When providing a search interface (F4), you can improve precision significantly by classifying a user’s query, assuming you are able to classify your content. If you have a category taxonomy and labeled queries, you can train a classifier in order to dynamically assign a category to a query.
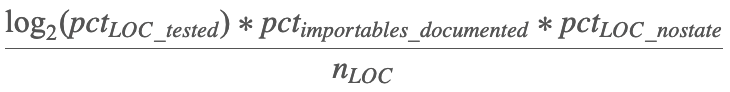
Have you ever set an objective function for code refactoring, where, for every proposed total change (e.g. reviewable pull request), you seek to maximize the change in this function? An example: 1 \ \log_2(pct_{LOC\ tested}) * pct {importables\ documented} * pct {LOC\ nostate} \over n {LOC} \ Good (numerator stuff): Percent Lines of Code (LOC) covered by a test.
Some energy infrastructure emits carbon. Some data infrastructure emits complexity. There is essential carbon emission, like humans exhaling CO 2 . And there is incidental, non-essential carbon emission, like humans burning fossil fuels. There is essential complexity in data (and software code), like that pertaining to modeling your subject matter and your application domain.
I am beginning to walk through each question of the FAIR Implementation Profile (FIP) Ontology. My goal is to construct and share a populated model of people’s articulations – aka declarations – of choices they’ve made or with challenges they face with regard to addressing each question, as well as the considerations they associate with any such choice or challenge.
The Archival Resource Key (ARK) system is an alternative to the Handle system to satisfy FAIR’s F1 Principle. Similar to the Handle system, naming authority for ARKs is distributed by allotting prefixes.
The Handle system is a popular choice for the assignment and resolution of globally unique, persistent identifiers. Governance is centralized with the DONA Foundation, and administration is distributed among so-called Credentialed Multi-Primary Administrators (MPAs), of which there are currently nine. You’ve likely heard of at least one MPA: the International DOI Foundation. Each MPA is assigned a number.
What globally unique, persistent, resolvable identifiers do you use for datasets? I want to know about either (a) a challenge you’re facing, and what you’ve tried; or (2) a choice you recently made, and how it’s going. Context: For each question of the FAIR Implementation Profile (FIP) Ontology, I want to collect and discuss folks’ choices and challenges on my podcast, Machine-Centric Science.
I keep confusing findability and discoverability. It seems that findability is often equated to known-item search, and discoverability to exploratory search. Known-item search is compatible with “instant search”, aka search-as-you-type interfaces. Exploratory search is compatible with “autocomplete” (incl. re-spelling, infix matching, synonym substitution, etc.) interfaces.
Is an ontology “better” than a relational data model? “More expressive power” doesn’t always mean “better”. However, ontologies allow you to ratchet up power while keeping logic in data structures.
Leave beacons in your code. I would have avoided a silly error if a variable named xgb_train_data would have been named, for example, xgb_train_data_filepath instead. When you can’t leave globally unique, persistent, resolvable identifiers (GUPRIs), mind your beacons. References: F. Hermans, The Programmer’s brain: what every programmer needs to know about cognition , pp28-30. Shelter Island, NY: Manning, 2021.