Since I have gotten into the habit of quoting some of my posts in other contexts, I have started to also archive them using WebCite.
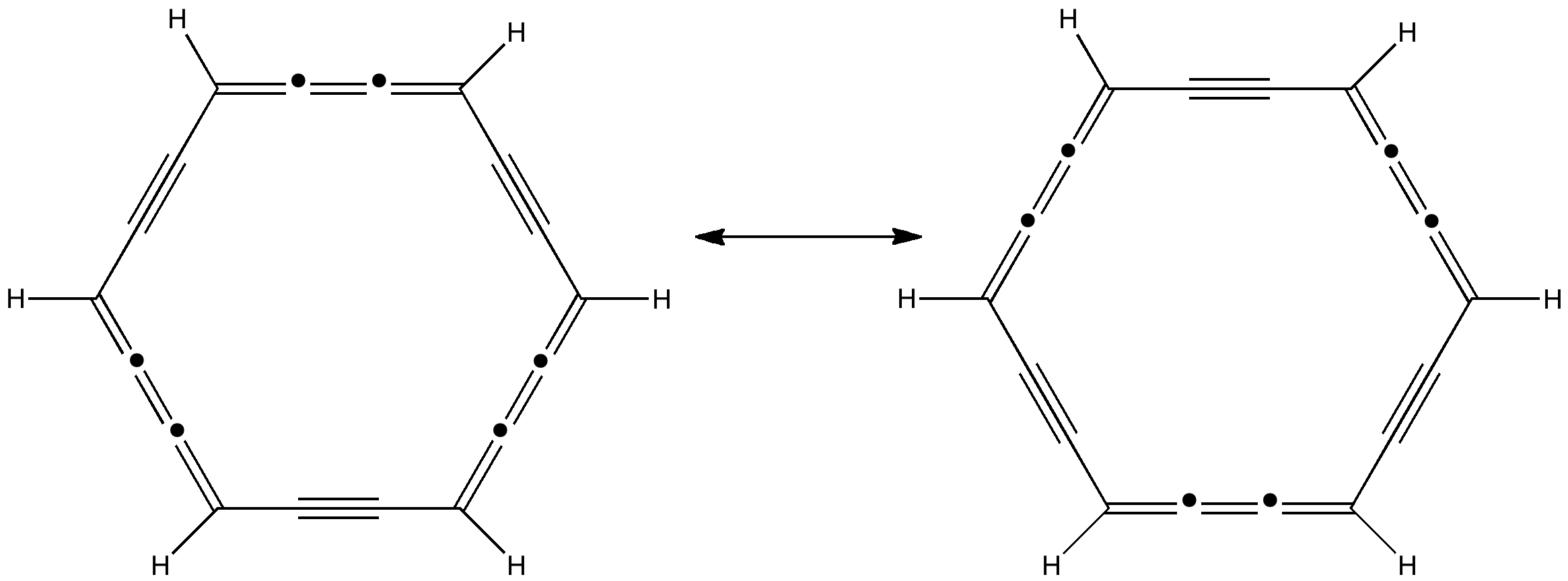
Some molecules, when you first see them, just intrigue. So it was with carbobenzene, the synthesis of a derivative of which was recently achieved by Remi Chauvin and co-workers (DOI: 10.1002/chem.200601193). Two additional carbon atoms have been inserted into each of the six C-C bonds in benzene.
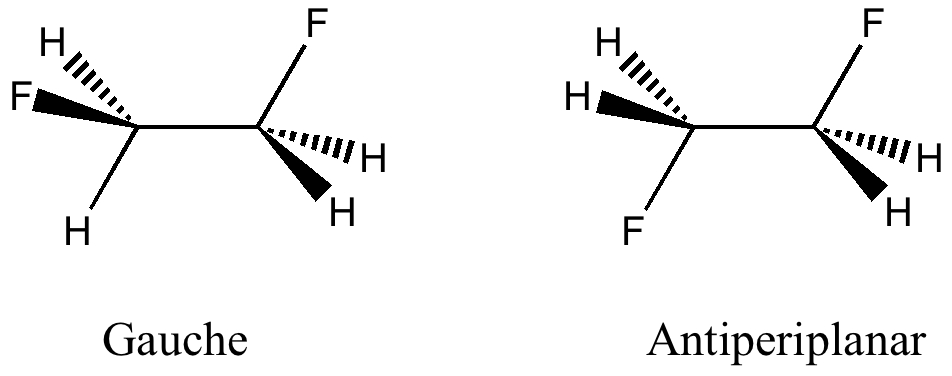
Here I offer another spin-off from writing a lecture course on conformational analysis. This is the famous example of why 1,2-difluoroethane adopts a gauche rather than antiperiplanar conformation.
One of the (not a few) pleasures of working in a university is the occasional opportunity that arises to give a new lecture course to students. New is not quite the correct word, since the topic I have acquired is Conformational analysis.
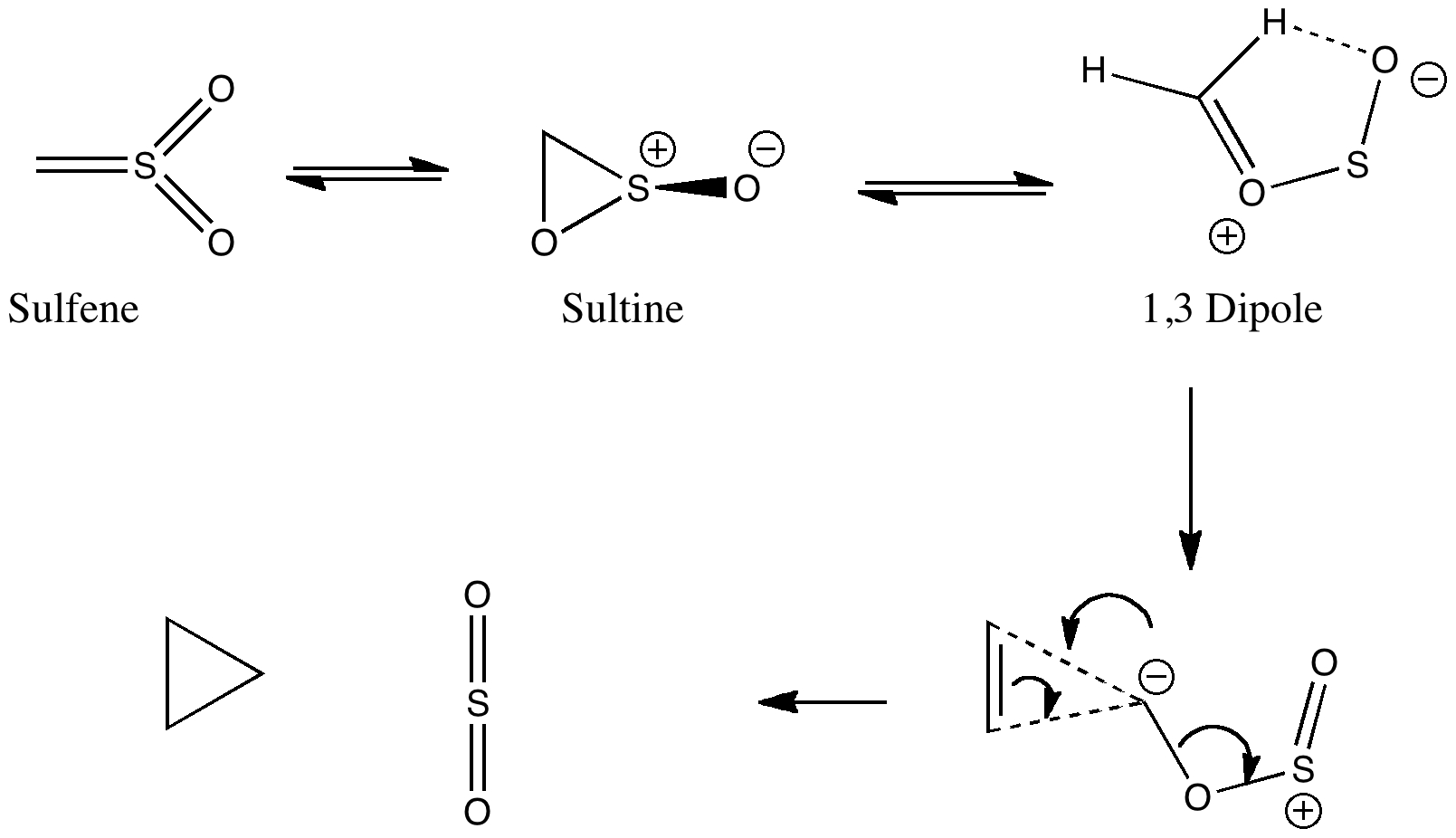
One future vision for chemistry over the next 20 years or so is the concept of having machines into which one dials a molecule, and as if by magic, the required specimen is ejected some time later. This is in some ways an extrapolation of the existing peptide and nucleotide synthesizer technologies and sciences.
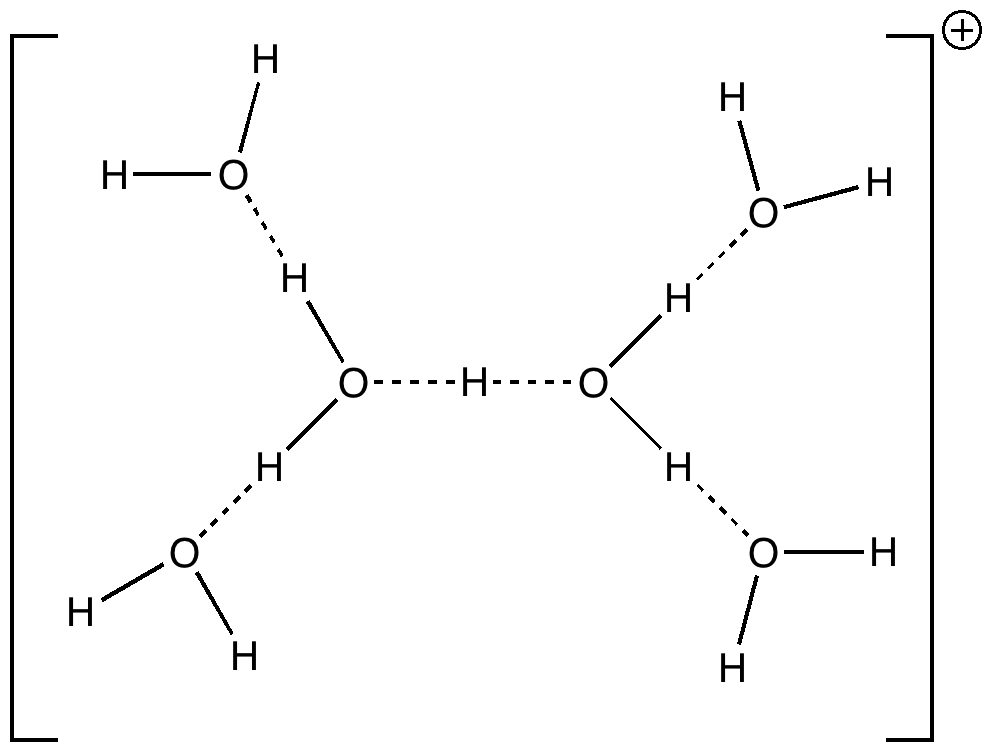
Stoyanov, Stoyanova and Reed recently published on the structure of the hydrogen ion in water.
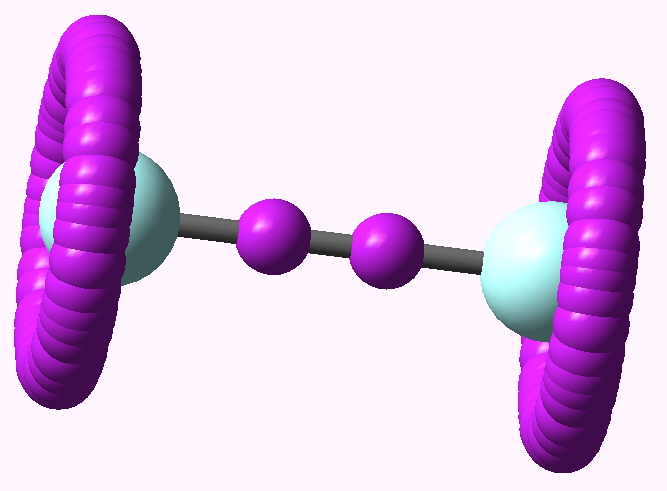
In the previous post, I ruminated about how chemists set themselves targets. Thus, having settled on describing regions between two (and sometimes three) atoms as bonds, they added a property of that bond called its order. The race was then on to find molecules which exhibit the highest order between any particular pair of atoms.
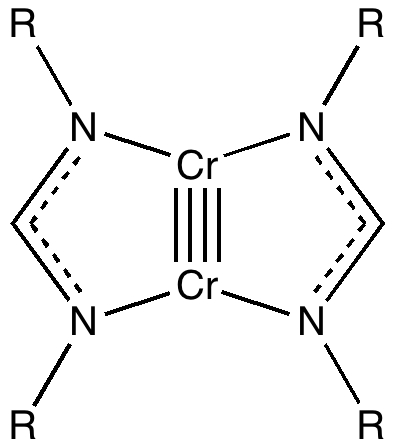
Climbers scale Mt. Everest, because its there, and chemists have their own version of this. Ever since G. N. Lewis introduced the concept of the electron-pair bond in 1916, the idea of a bond as having a formal bond-order has been seen as a useful way of thinking about molecules.

In an earlier post, I re-visited the conformational analysis of cyclohexane by looking at the vibrations of the entirely planar form (of D6h symmetry). The method also gave interesting results for the larger cyclo-octane ring. How about a larger leap into the unknown?
Scientists write blogs for a variety of reasons.
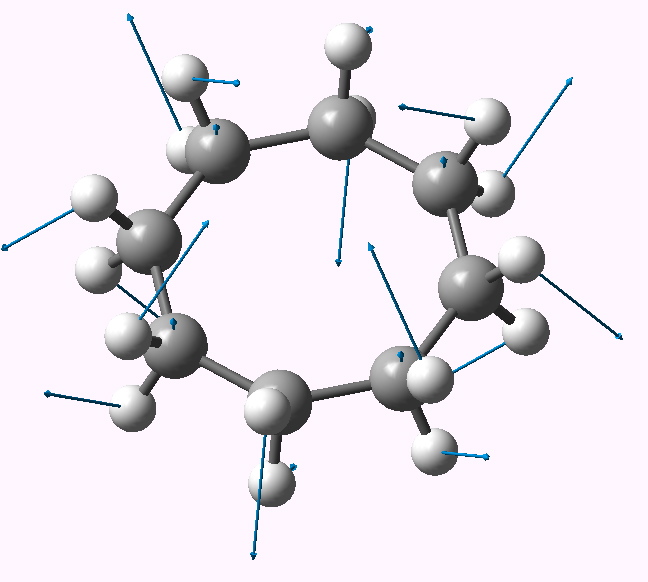
In the previous post, I suggested that inspecting the imaginary modes of planar cyclohexane might be a fruitful and systematic way in which at least parts of the conformational surface of this ring might be probed. Here, the same process is conducted for cyclo-octane.